Bauhinia racemosa (Bidi Leaf Tree)
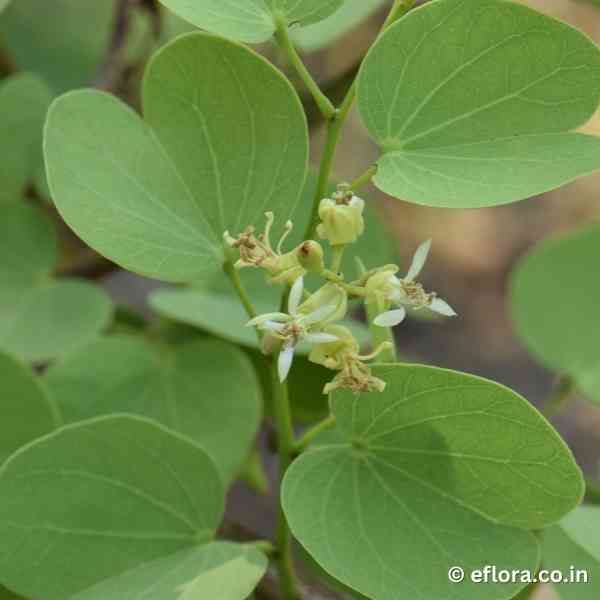
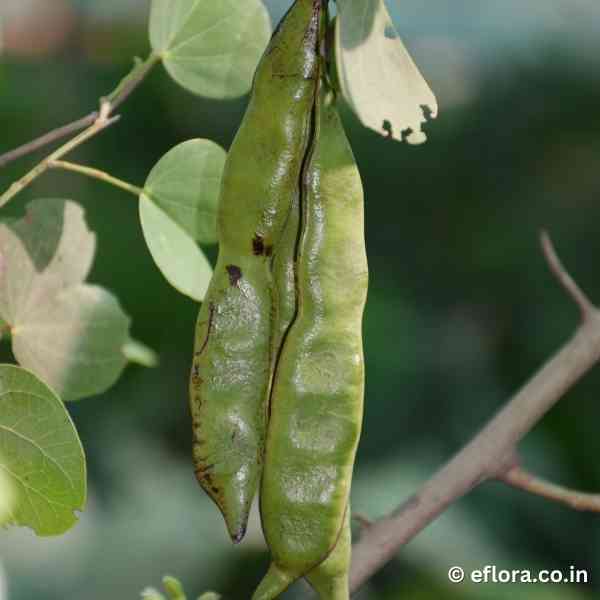
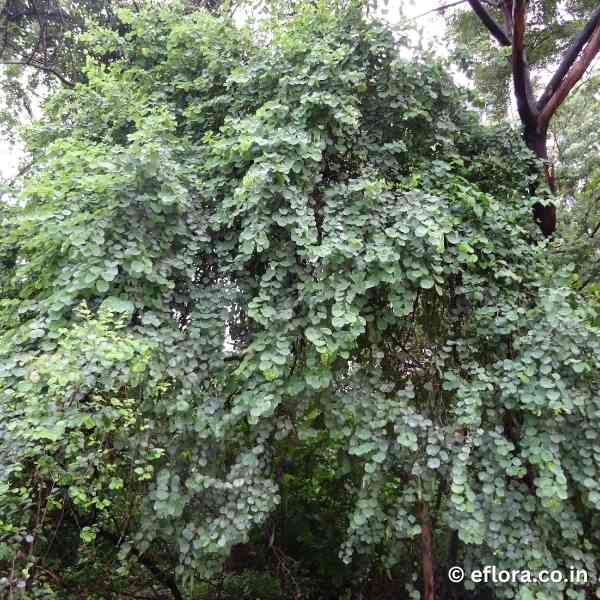
A small tree with short, somewhat crooked bole and a spreading crown. Leaves broadly orbicular, bifid at apex. Inflorescence a lateral or terminal raceme. Flowers small, petals creamy, fertile stamens 10. Fruit linear, sub-cylindric, woody, up to 20 cm long.
Flowering & Fruiting: October-April.
Etymology: The genus name Bauhinia is named after two illustrious Swiss botanists, the brothers John and Caspar Bauhin. John (1541-1613) was responsible among other works for the great Historia Plantarum, published nearly forty years after his death. Caspar (1560-1624) produced a valuable collection of synonyms. It has been suggested that the twin leaflobes of the plant typify the two brothers. . The specific epithet racemosa originates from “racemus,” describing its inflorescence type where flowers are arranged along an elongated central axis.